Abbreviations and acronyms are useful tricks in communication. They occur in every language and certainly also in English. Whether you’re writing an email or typing quickly on your smartphone, short words or expressions make life easier – and more fun!
According to abbreviationfinder, abbreviations are simply the result of word abbreviations (eg about instead of about) and are easy to understand, but acronyms can be a bit confusing and less intuitive. They consist of the first letter of each word in a sentence and are often capitalized, creating a new expression – LOL, for example, is an acronym for Laughing Out Loud.
English acronyms can be used in both formal and informal contexts; so it is absolutely necessary for English speakers to at least recognize and understand them. And of course, if you want to use them yourself, it helps to write a little bit faster – you’ll sound accomplished right away! Here are 10 very common English acronyms you should know:
1. BRB
BRB is really something you can say in any context, but this acronym is mainly used in conversations with friends. WhatsApp back and forth with your buddy and your father suddenly have to speak to you? Don’t worry, let your friend know: BRB.
2. ASAP
This one might freak you out if it’s in an email from your boss. When you read “can you finish this ASAP?” well, then get to work quickly, because your deadline is As Soon As Possible – a little euphemism for “now” or even “last Thursday”!
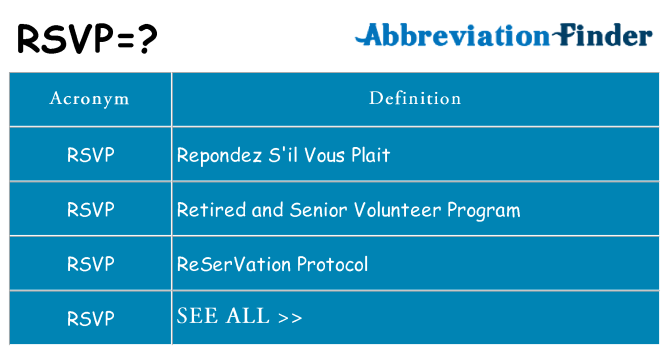
3. RSVP
You’ll find these on many meeting invitations, from weddings and parties to office gatherings and meetings. As with many English expressions, this comes from French and stands for Répondez s’il vous plait – it’s simply a request to respond and either confirm or cancel your presence.
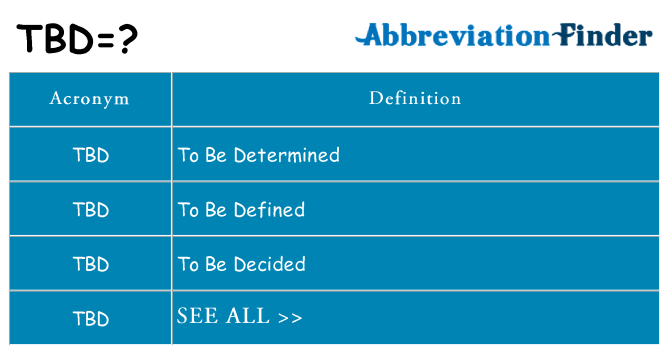
4. TB/TBD
The same invitation where you were asked for an RSVP can say that the meeting is To Be Confirmed, so you don’t have to book your taxi yet! For example, topics can also be mentioned in the minutes of a meeting: To Be Discussed.
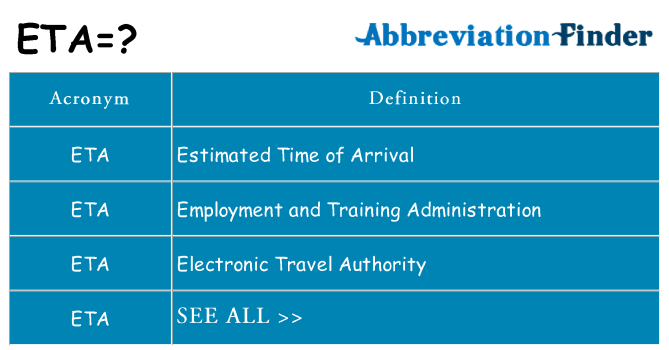
5. ETA
ETA is actually a very common acronym in the transportation world. It refers to an Estimated Time of Arrival. However, feel free to use it if you want to specify what time you will be somewhere (“Yes, I know we’re meeting at 6 PM, but I’m afraid my new ETA is going to be 7 PM…”)
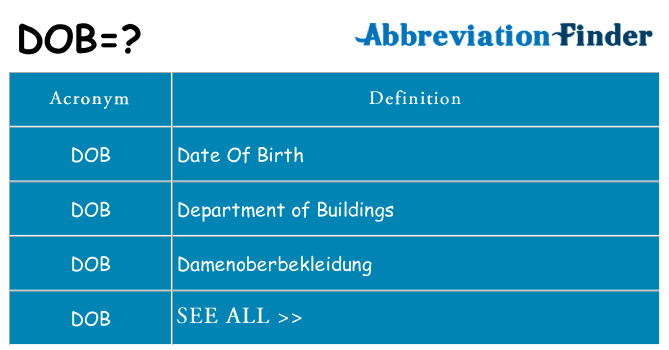
6. DOB
This acronym is really strange. It sounds like an alien’s name or like a kid-friendly expression for “poo.” Unfortunately, it’s less entertaining – DOB stands for Date Of Birth and you’ll usually find it on forms that require you to enter personal information.
7. IMO
Who doesn’t have a few opinions that should definitely be shared with others? This will let you know quickly! In My Opinion precedes such an opinion, or the even more polite IMHO which stands for In My Humble Opinion.
8. AKA
This acronym can be especially useful if you like to give nicknames – The Boss, aka ‘my mother’”. Also known as comes in handy if you’re being a little cheeky, for example: “To the customer for the smartest person here, aka ‘Me’”.
9. DIY
If you are such a handyman and like to repair electricity or redecorate your house yourself instead of using a company, know that you are a Do It Yourself person.
10. FOMO
Picture it for a second: it’s Friday and your friends are going out for a night, but you’re tired and you really don’t want to be late. So you’re thinking about not going. And then it starts to itch, because afterwards you might regret that you missed this legendary outing. Exactly this feeling is FOMO – Fear Of Missing Out.
Geography: 50 States of United States
- Bonanza History Timeline - 2007: Bonanza is founded by Bill Harding and Mark Dorsey in Seattle, Washington. The platform initially starts as an online marketplace for handmade and artisanal goods, aiming to provide a unique alternative to larger e-commerce platforms. 2008: Bonanza expands its product categories to include a wider range of items, including collectibles, antiques, and fashion accessories....
- Financial Accounting Acronyms - Financial accounting is the backbone of any business, providing insights into its financial health and performance. Understanding common accounting acronyms is essential for both beginners and experienced professionals in the field. In this guide, we’ll list 20 financial accounting acronyms, provide an overview of each term, offer tips for beginners and experienced professionals, and recommend...
- Geography of Isle of Wight County, Virginia - Isle of Wight County, located in the southeastern part of the state of Virginia, is a region distinguished by its rich history, scenic landscapes, and charming rural character. From its sprawling farmlands and winding rivers to its historic towns and waterfront communities, Isle of Wight County offers residents and visitors alike a unique blend of...
- Geography of Windham County, Vermont - Geography of Windham County, Vermont Windham County, situated in the southeastern part of Vermont, is a region characterized by its diverse geography, including rolling hills, dense forests, and meandering rivers. Covering an area of approximately 798 square miles, Windham County is nestled within the Green Mountains and serves as a rural community with a rich...
- Geography of Johnston County, Oklahoma - Johnston County, located in south-central Oklahoma, is characterized by its diverse geography, including rolling hills, fertile plains, and the winding rivers that traverse the region. From its agricultural landscapes and natural beauty to its historic sites and cultural heritage, Johnston County offers a blend of rural charm and outdoor recreation that defines its identity. Geography:...
- Geography of Isanti County, Minnesota - Geography of Isanti County, Minnesota Isanti County is located in the east-central part of the state of Minnesota, United States. It is known for its diverse landscapes, including rolling prairies, wooded areas, and numerous lakes and rivers. Covering an area of approximately 452 square miles, Isanti County offers a mix of rural charm, natural beauty,...
- What is Neon Clock? - The neon clock is an iconic and timeless piece of decor that combines the allure of neon lighting with the functionality of a traditional clock. With its vibrant colors, eye-catching glow, and retro charm, the neon clock has become a beloved fixture in bars, diners, game rooms, and home decor collections around the world. In...
- Facts about Yiwu Futian Market - Yiwu Futian Market, situated in the heart of Yiwu City in Zhejiang Province, China, stands as one of the largest wholesale markets globally. Renowned for its extensive range of commodities, it has earned the moniker “International Trade City.” Spanning over 4 million square meters, Futian Market is a bustling hub of trade, attracting buyers and...
- Geography of Craighead County, Arkansas - Geography of Craighead County, Arkansas Craighead County, located in the northeastern part of Arkansas, is a region defined by its diverse geography, rich agricultural heritage, and vibrant communities. Spanning approximately 713 square miles, it is one of the larger counties in the state. The county is known for its flat plains, fertile farmland, and abundance...
- Geography of Canadian County, Oklahoma - Canadian County, located in central Oklahoma, is a region characterized by its diverse geography, semi-arid climate, and significant waterways. From its rolling plains and fertile farmland to its meandering rivers and expansive lakes, the county’s geography plays a crucial role in shaping its economy, culture, and way of life. In this comprehensive overview, we’ll explore...